-22%
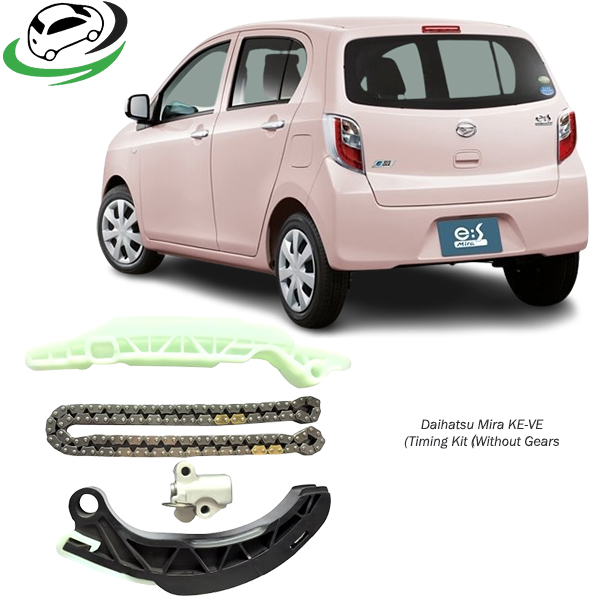
Get Daihatsu Mira KE-VE Timing Kit (Without Gears) 13506-B2010 in Kenya
A timing kit, also known as a timing belt kit or timing chain kit, is a crucial component in an internal combustion engine’s timing system. It consists of various components designed to ensure precise synchronization and operation of the engine’s valves and pistons. Here’s a comprehensive exploration of what a timing kit is, its components, function, types, importance, maintenance, and related considerations.
Definition and Functionality
Definition
A timing kit refers to a set of components used to control the timing of a combustion engine’s valves in relation to the engine’s pistons. It typically includes a timing belt or chain, tensioner, idler pulleys, and sometimes water pump. The kit ensures that the engine’s valves open and close at the correct times in sync with the piston’s movement.
Functionality
The primary function of a timing kit is to synchronize the rotation of the camshaft(s) and crankshaft in an engine. This synchronization is crucial for proper valve operation, ensuring that the intake and exhaust valves open and close at the correct times during the engine’s four-stroke cycle (intake, compression, power, exhaust).
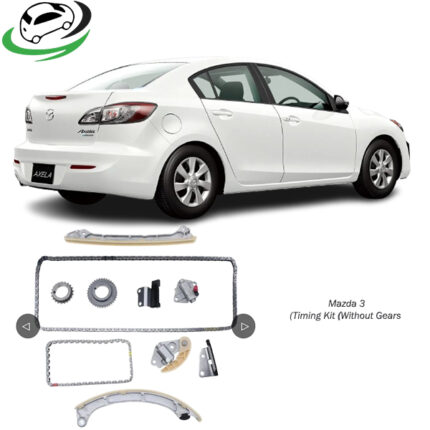
Components of a Timing Kit
Timing Belt or Timing Chain
- Timing Belt: A toothed rubber belt that connects the camshaft(s) to the crankshaft, ensuring precise synchronization of their rotations. It’s typically made of reinforced rubber with teeth on the inner side to grip gears without slipping.
- Timing Chain: A metal chain with links that engage with teeth on the camshaft(s) and crankshaft gears. Timing chains are more durable and commonly used in engines designed for longevity and higher performance.
Tensioner
- A component that maintains proper tension on the timing belt or chain to prevent slack and ensure reliable operation. It can be hydraulic or mechanical, depending on the engine design.
Idler Pulleys
- Pulleys used to guide and support the timing belt or chain. They help maintain proper alignment and tension throughout the timing system.
Water Pump (in some kits)
- In some vehicles, the timing kit may include a water pump. This is often recommended during timing belt replacement since the water pump is typically driven by the timing belt. Replacing both components simultaneously can save on labor costs and prevent future maintenance issues.
Types of Timing Kits
Timing Belt Kit
- Includes a timing belt, tensioner, idler pulleys, and sometimes a water pump. Common in vehicles with timing belts that require periodic replacement according to manufacturer recommendations (typically every 60,000 to 100,000 miles).
Timing Chain Kit
- Includes a timing chain, tensioner, and idler pulleys. Timing chains are more durable than timing belts and are commonly found in engines designed for longevity and higher performance, such as many modern vehicles.
Timing Belt and Water Pump Kit
- Combines a timing belt kit with a water pump replacement. Recommended when the water pump is driven by the timing belt and is approaching the end of its service life to prevent future maintenance issues.
Importance of a Timing Kit;
1. Synchronization of Engine Components
Valve Timing
A timing kit, whether it includes a timing belt or timing chain, ensures that the camshaft(s) and crankshaft rotate in perfect synchronization. This synchronization is vital because it determines when the engine’s intake and exhaust valves open and close in relation to the piston’s position. Proper valve timing allows for efficient intake of air and fuel, precise combustion timing, and effective expulsion of exhaust gases.
Prevention of Valve-Piston Collision
Incorrect timing, such as a malfunctioning or worn-out timing belt or chain, can lead to the misalignment of valve timing. In worst-case scenarios, this can cause the valves to remain open when the piston is coming up, leading to a collision between the valve and piston. Such collisions can cause severe damage to the engine, necessitating expensive repairs or even complete engine replacement.
2. Engine Performance and Efficiency
Optimal Combustion Cycle
Precise timing provided by a well-maintained timing kit ensures that the engine operates at its peak efficiency. When valves open and close at the correct times, the combustion process is optimized. This results in smoother engine operation, improved fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. Proper combustion also enhances engine power output and responsiveness, contributing to overall vehicle performance.
Timing Accuracy
Modern engines rely on precise timing to meet stringent emissions regulations and performance standards. A timing kit that maintains accurate valve timing allows the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize fuel injection timing and other parameters. This precision contributes to cleaner exhaust emissions and compliance with environmental standards.
3. Engine Reliability and Longevity
Prevention of Catastrophic Engine Damage
A failed timing belt or chain can lead to catastrophic engine damage, such as bent valves, damaged pistons, or even a cracked engine block. The cost of repairing such damage is significantly higher than the cost of preventative maintenance. Regular replacement of the timing kit components as recommended by the manufacturer helps prevent these costly failures.
Longevity of Engine Components
Properly maintained timing components contribute to the longevity of other engine components. By ensuring that valves and pistons operate smoothly without interference, the timing kit minimizes wear and tear on critical engine parts. This extends the lifespan of components such as valve seals, camshaft bearings, and piston rings, reducing the frequency of repairs and increasing the overall reliability of the engine.
4. Maintenance of Engine Timing Stability
Tension and Alignment Control
A timing kit includes components like tensioners and idler pulleys that help maintain proper tension and alignment of the timing belt or chain. Over time, these components can wear out or lose their effectiveness, leading to slack in the timing system. This can result in timing fluctuations, which compromise engine performance and reliability. Regular replacement of these components as part of the timing kit ensures that timing stability is maintained.
Water Pump Integration
In many engines, the water pump is driven by the timing belt. Including the water pump in the timing kit replacement ensures that both components are replaced simultaneously. This preventative maintenance approach not only saves on labor costs but also prevents potential coolant leaks or water pump failures that could lead to overheating and engine damage.
5. Cost-Effective Maintenance Strategy
Preventative Maintenance
Replacing the timing kit components at recommended intervals is a proactive maintenance strategy. It prevents unexpected timing belt or chain failures that can result in costly repairs and downtime. Compared to the expense of repairing engine damage caused by a failed timing component, regular timing kit replacement is a cost-effective investment in engine longevity and reliability.
Comprehensive Replacement
When replacing a timing kit, it’s often recommended to inspect and replace associated components such as seals and gaskets. This ensures a comprehensive maintenance approach that addresses potential sources of future issues and prolongs the overall reliability of the engine.
Maintenance and Replacement
Replacement Interval
- Timing belt replacement intervals vary by manufacturer and vehicle model but typically range from 60,000 to 100,000 miles. Timing chains generally last longer but may require inspection at higher mileage intervals.
Signs of Timing Kit Issues;
- Engine Misfires: Misfires occur when the combustion process is disrupted due to improper timing. This can manifest as rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, or noticeable vibrations while driving.
- Engine Noise: A timing belt or chain that is worn, loose, or misaligned can produce unusual noises. These may include rattling, ticking, or slapping sounds coming from the engine compartment. The noise can be more pronounced during startup or acceleration.
- Visible Wear on Timing Belt: For engines with timing belts, visual inspection can reveal signs of wear and damage. Look for cracks, fraying, or shiny spots on the belt’s surface. Excessive wear may also cause the timing belt to become loose or stretch.
- Engine Won’t Start or Hard Starting: A worn or broken timing belt or chain can prevent the engine from starting altogether. In some cases, the engine may crank but fail to start due to improper valve timing caused by a timing kit issue.
- Loss of Power: Incorrect timing can lead to inefficient combustion, resulting in reduced engine power and performance. This may be noticeable during acceleration or when climbing hills.
- Engine Overheating: In engines where the water pump is driven by the timing belt, a failing timing belt can lead to water pump failure. This can cause coolant circulation issues, leading to engine overheating.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): The check engine light may illuminate due to timing-related issues. The engine control unit (ECU) detects timing discrepancies and stores diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to camshaft position, crankshaft position, or misfire detection.
- Oil Leaks: A leaking front engine seal or camshaft seal can result from wear or damage to the timing belt or timing chain cover. Oil leaks may be visible around the timing cover or near the front of the engine.
- Poor Fuel Efficiency: Timing kit issues can lead to inefficient combustion, causing the engine to burn more fuel than necessary. This results in decreased fuel efficiency and increased fuel consumption.
- Visible Oil on Timing Components: Oil contamination on the timing belt or timing chain can indicate a leak from nearby seals or gaskets. Oil can accelerate wear on the timing components and affect their performance.
- Physical Damage to Components: Inspecting the timing belt or chain, tensioner, idler pulleys, and associated components may reveal physical damage, such as cracks, breaks, or signs of excessive wear. This is often evident during routine maintenance inspections.
- Engine Vibration or Rough Running: Improper timing can cause the engine to run rough or vibrate excessively. This may be felt throughout the vehicle, particularly at idle or low speeds.
- Timing Belt Age and Mileage: For timing belts, knowing the manufacturer’s recommended replacement interval is crucial. Over time, even without visible signs of wear, timing belts can degrade due to age and mileage, necessitating replacement to prevent unexpected failures.
Replacement Procedure
Timing Belt Replacement
- Preparation: Ensure the engine is cool, disconnect the battery, and secure necessary tools.
- Component Removal: Remove necessary components blocking access to the timing cover.
- Belt Removal: Loosen tensioner, remove old belt, and inspect components.
- Installation: Install new belt, tensioner, idler pulleys, and water pump (if applicable).
- Tension Adjustment: Follow manufacturer specifications to set proper tension.
- Testing: Rotate engine manually to ensure proper alignment and tension.
Professional vs. DIY
- Timing kit replacement can be complex and requires precise timing and tension adjustments. While DIY enthusiasts with mechanical experience may tackle timing belt replacements, timing chain replacements often require specialized tools and expertise, making professional installation advisable for many vehicle owners.
Follow us on Facebook for more parts.