-13%
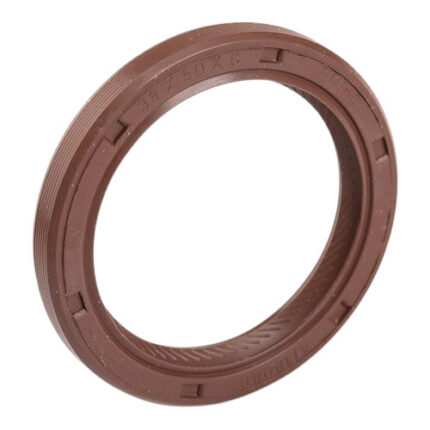
Get Genuine Rear Engine Oil Seal 90311-73005 in Kenya
The engine oil seal is a crucial component in an internal combustion engine, designed to prevent oil leaks and maintain the necessary lubrication of engine components. This small but essential part plays a significant role in ensuring engine efficiency and longevity. This article delves into the function, importance, materials, common issues, replacement process, and maintenance of engine oil seals.
Function and Importance
The primary function of the engine oil seal is to prevent engine oil from leaking out of the engine. These seals are typically found in various parts of the engine, such as the crankshaft, camshaft, and other rotating or reciprocating components. Their key roles include:
- Sealing: They create a tight seal around the rotating shafts to prevent oil from leaking out of the engine.
- Contaminant Prevention: By sealing the engine, they prevent dirt, dust, and other contaminants from entering and causing wear or damage.
- Pressure Maintenance: They help maintain the correct pressure within the engine to ensure efficient oil circulation and lubrication of moving parts.
Materials
Engine oil seals are made from materials that offer high resistance to heat, oil, and wear. Common materials include:
- Nitrile Rubber (Buna-N): Offers good resistance to oil and fuel and is cost-effective. Suitable for a wide range of temperatures and pressures.
- Silicone Rubber: Known for excellent heat resistance and flexibility. Often used in high-temperature applications.
- Fluoroelastomer (Viton): Provides superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and oil. Ideal for high-performance engines.
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): Also known as Teflon, this material is highly resistant to chemicals and heat and has low friction properties.
Common Issues
Over time, engine oil seals can develop issues due to wear, heat, and other factors. Common problems include:
- Oil Leaks: The most obvious sign of a failing oil seal is an oil leak. This can manifest as oil spots under the vehicle or visible oil on engine components.
- Engine Noise: A worn seal can lead to insufficient lubrication, causing increased friction and noise from the engine.
- Overheating: Oil leaks can result in low oil levels, reducing the engine’s ability to dissipate heat effectively, potentially leading to overheating.
- Contamination: A damaged seal can allow dirt and debris to enter the engine, causing wear and damage to internal components.
Replacement Process
Replacing an engine oil seal is a critical maintenance task that should be performed promptly if signs of wear or leakage are detected:
- Preparation: Ensure the engine is cool and gather the necessary tools and replacement seals. Disconnect the battery to prevent accidental starts.
- Access: Remove any components obstructing access to the faulty oil seal. This may include the timing cover, belts, pulleys, or other engine components.
- Removal: Carefully remove the old seal using appropriate tools, such as a seal puller or screwdriver. Avoid damaging the surrounding surfaces.
- Inspection: Inspect the sealing surface and shaft for wear or damage. Clean the area thoroughly to ensure a proper seal.
- Installation: Apply a thin layer of oil to the new seal and carefully press it into place. Use a seal driver or a socket of appropriate size to ensure even installation.
- Reassembly: Reinstall any components removed during the process, ensuring all bolts and fittings are tightened to manufacturer specifications.
- Testing: Start the engine and monitor for leaks. Check oil levels and ensure there are no signs of oil leakage or abnormal engine noise.
Maintenance
Proper maintenance can extend the life of engine oil seals and prevent premature failure:
- Regular Inspections: Periodically check for signs of oil leaks around the seals and other engine components.
- Timely Oil Changes: Regular oil changes ensure clean oil, which reduces wear on the seals.
- Quality Parts: Use high-quality oil seals designed for your specific engine to ensure proper fit and durability.
- Proper Installation: Ensure seals are installed correctly, following the manufacturer’s specifications and using the right tools.
Follow us on Facebook for more parts.